AERIAL SURVEYS FOR MARINE WILDLIFE
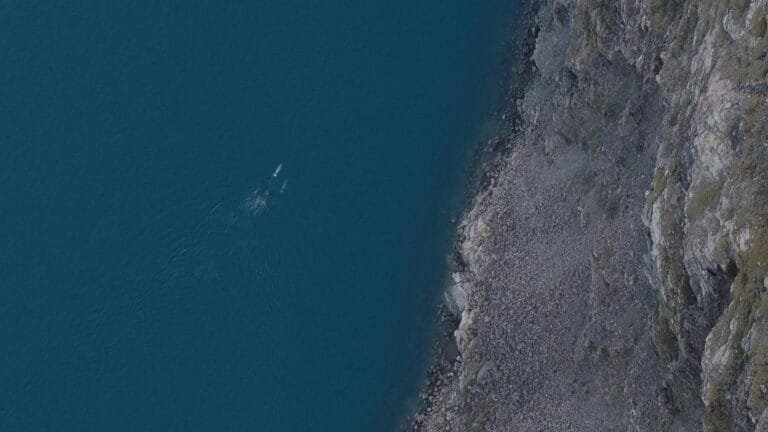
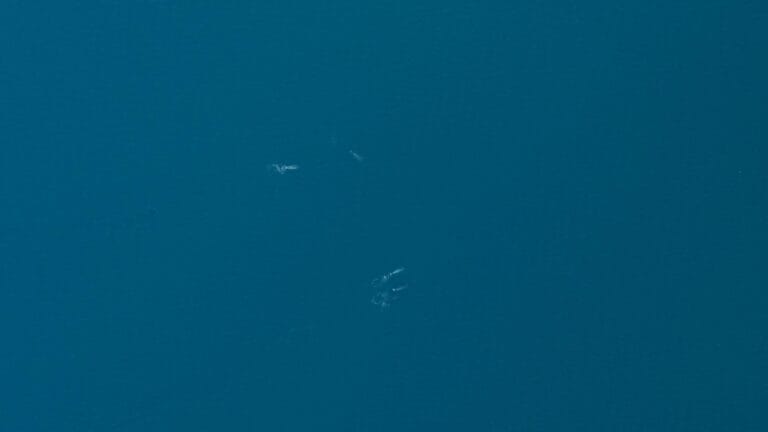
COUNTING WHALES FROM ABOVE
The Role of Wildlife Surveys in Conservation
Wildlife surveys play a crucial role in understanding biodiversity health and supporting effective ecological monitoring and management. By providing detailed insights across vast and often inaccessible areas, aerial photography has become an invaluable tool for inventorying animals, studying local biomes, and assessing vegetation health.
The degradation of natural habitats and loss of biodiversity are among the most pressing crises facing the planet today. These threats not only endanger species like whales but also have cascading impacts on ecosystems and, ultimately, human societies. Aerial wildlife surveys are vital for collecting the data needed to address these challenges, enabling researchers to monitor biodiversity and inform conservation efforts.
Limitation of Satellite Imagery in Wildlife Studies
While very-high-resolution (VHR) satellite imagery is a growing resource in wildlife studies, it comes with limitations. These include cloud cover interference, outdated imagery, and insufficient resolution for certain applications.
Aerial surveys can overcome these challenges through flexible, real-time, and high-resolution data collection tailored to specific project needs. This adaptability makes aerial photography a preferred method for many conservation efforts. Advanced multispectral imaging technology is transforming aerial wildlife monitoring. Infrared cameras, for example, enable night-time surveys and detect animals hidden from view, offering unparalleled insights into wildlife populations and behaviours.
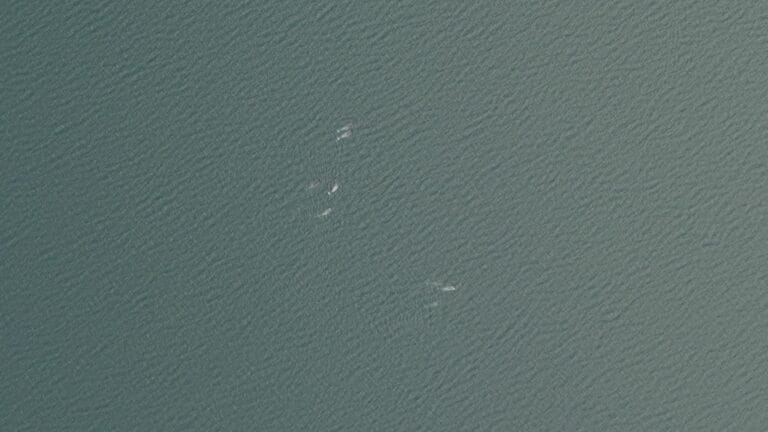
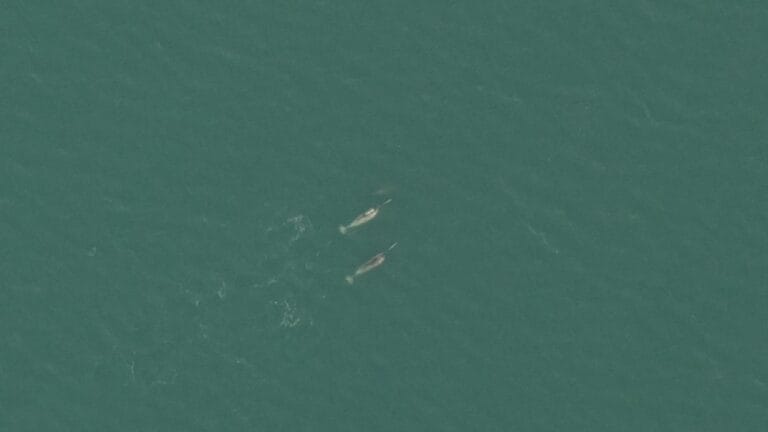
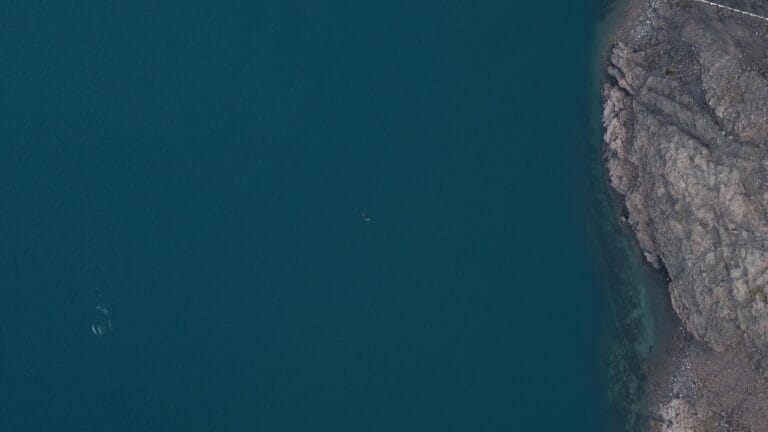
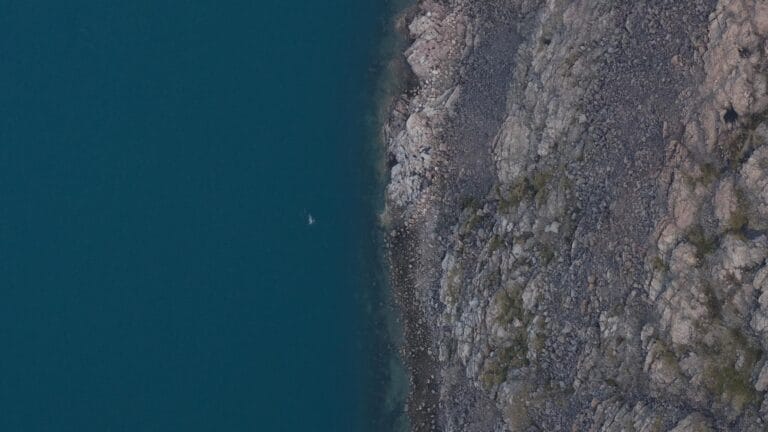
Whale Population Monitoring
Recently, we supported a multiyear whale study designed to assess the potential impact of shipping lanes on local whale populations’ spawning grounds and migration routes. By combining high-resolution imagery and precise survey planning, researchers are gaining a deeper understanding of whale population dynamics, migration patterns, and long-term trends. This information is critical for developing strategies to protect these marine giants.
While whales are a major focus of our marine wildlife surveys, the versatility of aerial imagery extends to other species as well. These methods are also used to count seals and track land-based wildlife in Africa, further showcasing their broad applicability in wildlife conservation.
The Future of Wildlife Surveys
By pairing cutting-edge technology with strategic survey planning, aerial wildlife surveys are making an invaluable contribution to biodiversity preservation. These efforts help ensure a future where humans and wildlife can thrive together.